微服务学习笔记
什么是微服务
https://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html
“Microservices” - yet another new term on the crowded streets of software architecture. Although our natural inclination is to pass such things by with a contemptuous glance, this bit of terminology describes a style of software systems that we are finding more and more appealing. We’ve seen many projects use this style in the last few years, and results so far have been positive, so much so that for many of our colleagues this is becoming the default style for building enterprise applications. Sadly, however, there’s not much information that outlines what the microservice style is and how to do it.
单体应用 -> 微服务应用
单体架构存在的缺点
- 复杂性逐渐变高
- 技术债务逐渐上升
- 部署速度逐渐变慢
- 阻碍技术创新
- 无法按需伸缩
什么是微服务
- Martin Fowler:简而言之,微服务架构风格这种开发方法,是以开发一组小型服务的方式来开发一个独立的应用系统。其中每个小型服务都运行在自己的进程中,并经常采用HTTP资源API这样轻量的机制来相互通信。这些服务围绕这些功能进行构建,并能通过全自动的部署机制来进行独立部署。这些微服务可以使用不同的语言来编写,并且可以使用不同的数据存储技术。对这些微服务我们仅做最低限度的集中管理。
- 微服务架构是一种架构模式,它提倡将单一应用程序划分成一组小的服务,服务之间相互协调、相互配合,为用户提供最终价值。每个服务运行在其独立的进程中,服务于服务间采用轻量级的通信机制互相沟通(通常是基于HTTP的RESTful API)。每个服务都围绕着具体的业务进行构建,并且能够独立地被部署到生产环境、类生产环境等。另外,应尽量避免统一的、集中式的服务管理机制,对具体的一个服务而言,应根据业务上下文,选择合适的语言、工具对其进行构建。
- 微服务是一种架构风格,一个大型复杂软件应用由一个或多个微服务组成。系统中的各个微服务可被独立部署,各个微服务之间是松耦合的。每个微服务仅关注完成一件任务并很好地完成该任务。在所有情况下,每个任务代表着一个小的业务能力。
微服务是一种架构风格
- 服务组件化(Componentization via Services)
- 服务围绕业务(Organized around Business Capabilities)
- 产品开发模式(Products not Projects)
- 轻量级通信机制(Smart endpoints and dumb pipes)
- 去中心化治理(Decentralized Governance)
- 去中心化数据设计(Decentralized Data Management)
- 故障处理设计(Design for failure)
- 演进式设计(Evolutionary Design)
- 基础设施自动化(Infrastructure Automation)
微服务的优点和挑战
- 开发简单
- 技术栈灵活
- 服务独立
- 按需扩展
- 运维复杂
- 数据一致性问题
- 集成测试复杂
- 重复代码
- 监控困难
微服务具备的特性
- 每个微服务可独立运行在自己的进程里
- 一系列独立运行的微服务共同构建起了整个系统
- 每个服务为独立的业务开发,一个微服务一般完成某个特定的功能,比如:订单管理,用户管理等
- 微服务之间通过一些轻量的通信机制进行通信,例如通过REST API或者RPC的方式进行调用
微服务的优点
- 易于开发和维护
- 启动较快
- 局部修改容易部署
- 技术栈不受限
- 按需伸缩
- DevOps
微服务带来的挑战
- 运维要求较高
- 分布式的复杂性
- 接口调整成本高
- 重复劳动
微服务的设计原则
- 单一职责原则
- 服务自治原则
- 轻量级通信原则
- 接口明确原则
SOA
很多人会把SOA和微服务搞混,甚至理解为同一个东西。实际上SOA已经面世20多年了,和微服务是不一样的,接下来去维基百科看看SOA到底是什么。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture
学技术,一定要去阅读原版的英文资料。
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a style of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. The basic principles of service-oriented architecture are independent of vendors, products and technologies.[1] A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online.
A service has four properties according to one of many definitions of SOA:[2]
- It logically represents a business activity with a specified outcome.
- It is self-contained.
- It is a black box for its consumers.
- It may consist of other underlying services.[3]
Different services can be used in conjunction to provide the functionality of a large software application,[5] a principle SOA shares with modular programming. Service-oriented architecture integrates distributed, separately-maintained and -deployed software components. It is enabled by technologies and standards that facilitate components’ communication and cooperation over a network, especially over an IP network.
SOA是一种软件设计风格,SOA包含了一些服务,服务是通过应用组件的形式,通过网络上的一些通信协议像向其他应用提供服务。不同的服务可以联合起来构成一个大型的应用,SOA遵循模块化编程,它的这种架构集成了分布式的,独自维护的,独自部署的软件组件。也是通过网络来通信的。
好像看起来SOA的和微服务的概念也没什么太大差别?
In SOA, services use protocols that describe how they pass and parse messages using description metadata. This metadata describes both the functional characteristics of the service and quality-of-service characteristics. Service-oriented architecture aims to allow users to combine large chunks of functionality to form applications which are built purely from existing services and combining them in an ad hoc manner. A service presents a simple interface to the requester that abstracts away the underlying complexity acting as a black box. Further users can also access these independent services without any knowledge of their internal implementation.[6]
在SOA里,服务是用元数据描述的服务的功能特性和质量特性。有没有想起wsdl实现的webservice?
SOA里有3个角色
- Service provider
- Service broker, service registry or service repository
- Service requester/consumer
SOA可以借助webservice实现,通过标准的internet协议,通过网络来访问这些功能。比如SOAP,Jini,CORBA,Rest
有很多技术都可以实现SOA,比如
- Web services based on WSDL and SOAP
- Messaging, e.g., with ActiveMQ, JMS, RabbitMQ
- RESTful HTTP, with Representational state transfer (REST) constituting its own constraints-based architectural style
- OPC-UA
- WCF (Microsoft’s implementation of Web services, forming a part of WCF)
- Apache Thrift
- SORCER
缺点
SOA已经被Web Service合并了,然而Web Service只是实现SOA的一种方式。在缺乏本地或二进制的数据传递调用的情况下,远程调用和效率都会变慢。XML是比较慢的,JSON相比XML会好一些。
有状态的服务不利于管理。
SOA主要的挑战是元数据的管理,服务于服务之间的通信会生成大量的消息。
难以测试。
微服务
微服务是现代化的SOA架构,用于构建分布式的软件系统。在微服务架构中的服务都是一些进程,它们之间是通过网络来进行通信去完成一个目标。这些服务使用技术不可知的协议,在服务内部去封装语言和框架。微服务是一种SOA的一种新的实现方式,从2014年开始变得流行起来(在引入DevOps后)。它强调的是持续的部署和其他敏捷的实现。
微服务没有统一的定义,但是有以下特征和原则
- fine-grained interfaces (to independently deployable services),
- business-driven development (e.g. domain-driven design),
- IDEAL cloud application architectures,
- polyglot programming and persistence,
- lightweight container deployment,
- decentralized continuous delivery, and
- DevOps with holistic service monitoring.
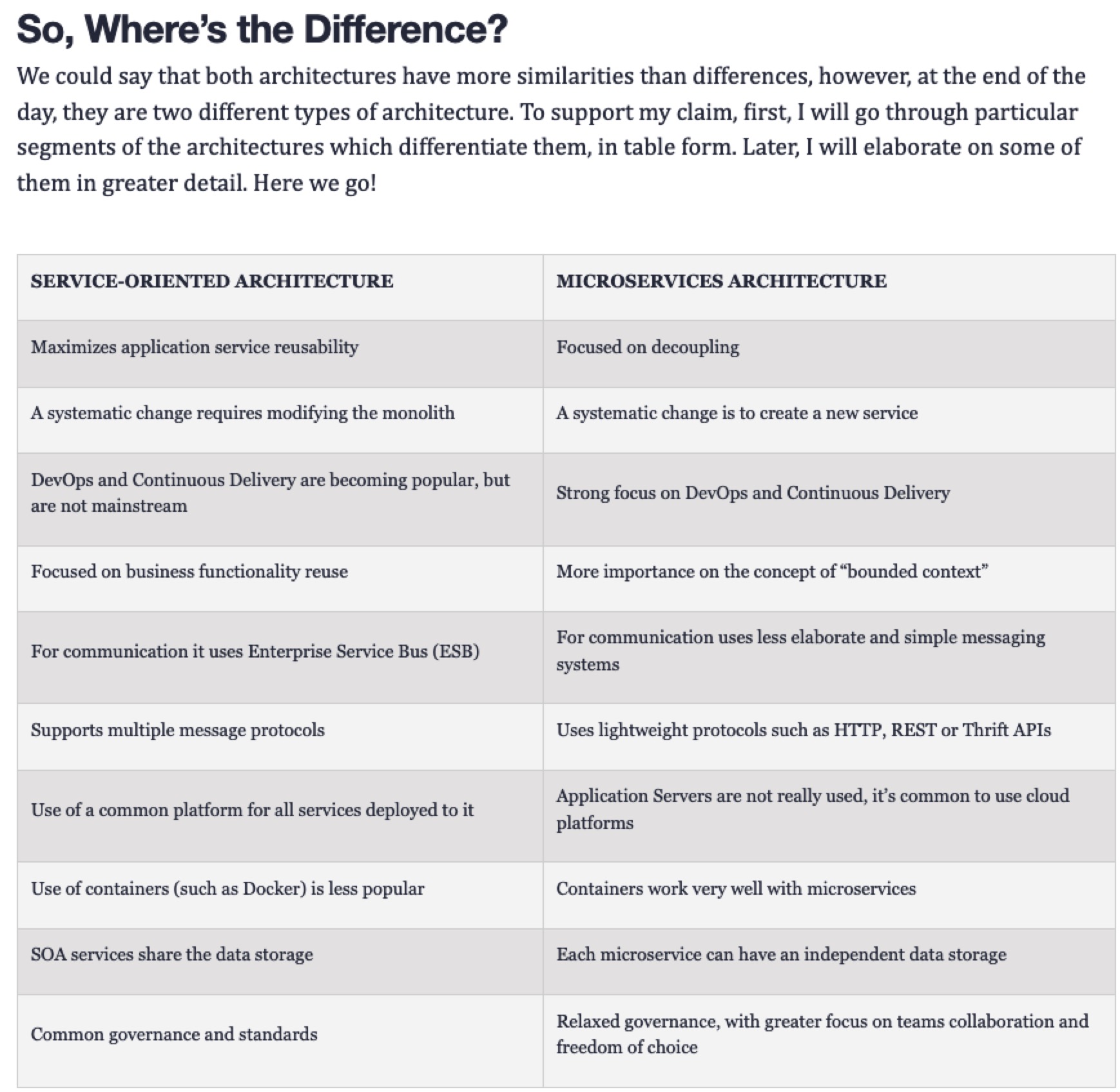
SOA和微服务的差异性
文章1
https://www.ibm.com/blogs/cloud-computing/2018/09/06/soa-versus-microservices/
The main distinction comes down to scope. To put it simply, service-oriented architecture (SOA) has an enterprise scope, while the microservices architecture has an application scope.
SOA着重点在企业范围,微服务着重点在应用范围。

从这个图可以看出来,SOA的范围更大,他关注的是应用与应用之间的关系。而微服务是应用内部的关联。
文章2
https://dzone.com/articles/microservices-vs-soa-is-there-any-difference-at-al
Service Oriented Architecture is less about how to modularize an application, and more about how to compose an application by integration of distributed, separately-maintained and deployed software components. It is enabled by technologies and standards that make it easier for components to communicate and cooperate over a network, especially an IP network.