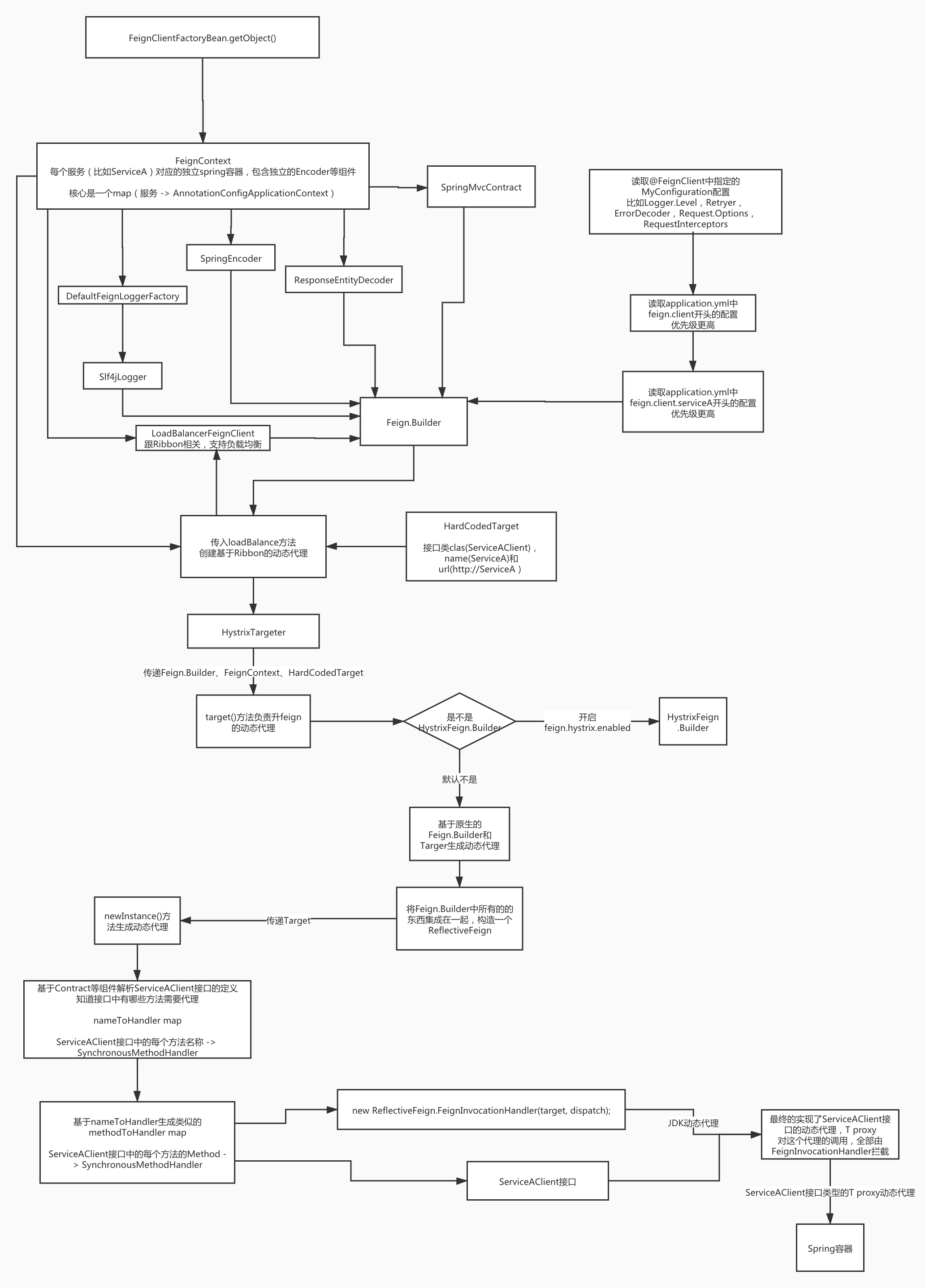
动态代理创建FeignClient的实例
在做完前面的事情以后,FeignClientFactoryBean已经被注册到Spring上下文中,根据Spring的原理,FactoryBean是用于构造复杂对象实例的一种工厂,可定制创建,初始化,刷新,销毁的各个过程。重点需要去看getObject()方法,看对象实例是如何产生的。
1 | // FeignClientFactoryBean.java |
下面先看下Feign.Builder是如何构造的
Feign.Builder构造过程以及Feign在SpringCloud中的默认组件
1 | // FeignClientFactoryBean.java |
步骤:
- 从ServiceA对应的Spring容器读取FeignLoggerFactory,默认是DefaultFeignLoggerFactory
- DefaultFeignLoggerFactory创建并设置Logger,是Slf4jLogger
- 从ServiceA对应的Spring容器读取并设置Feign.Builder,如果开启feign.hystrix.enabled配置,是HystrixFeign.Builder,默认是Feign.Builder
- 从ServiceA对应的Spring容器读取并设置Encoder,默认是SpringEncoder
- 从ServiceA对应的Spring容器读取并设置Decoder,默认是ResponseEntityDecoder
- 从ServiceA对应的Spring容器读取并设置Contract,默认是SpringMvcContract
- 读取并设置application.yml属性
超时、日志级别、拦截器等属性设置
1 | // FeignClientFactoryBean.java |
配置读取过程详解:
读取@FeignClient中指定的MyConfiguration配置,比如Logger.Level,Retryer,ErrorDecoder,Request.Options,RequestInterceptors。
读取application.yml中feign.client开头的配置,application.yml的优先级更高。
读取application.yml中feign.client.serviceA开头的配置,这个优先级最高
动态代理创建ServiceAClient的实例
根据配置构造好了Feign.Builder后,就要开始创建Feign.Client的实例
1 | // FeignClientFactoryBean.java |
步骤:
- 如果@FeignClient没有配置url属性,就将服务名拼接成http://ServiceA)这样的地址
- 构造了一个HardCodedTarget,包含了type:接口类class(ServiceAClient),name(ServiceA)和url(http://ServiceA),和Feign.Builder、FeignContext一起传入loadBalance。
1 | // FeignClientFactoryBean.java |
步骤:
从上下文获取了一个Client,通过IDEA强大的源码查看能力,找到一个实现类LoadBalancerFeignClient,取决于不同的实现,可能会由
DefaultFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration或者HttpClientFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration或者OkHttpFeignLoadBalancedConfiguration定义的,通过FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration的@Import注解导入。默认是Default开头的。LoadBalancerFeignClient就是基于Ribbon,可负载均衡的。1
2
3
4
5//Order is important here, last should be the default, first should be optional
public class FeignRibbonClientAutoConfiguration {从Spring容器中获取到targeter动态代理的组件,Targeter的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21// FeignAutoConfiguration.java
// 这个条件明显是成立的,所以代码拿到的肯定是HystrixTargeter
protected static class HystrixFeignTargeterConfiguration {
public Targeter feignTargeter() {
return new HystrixTargeter();
}
}
protected static class DefaultFeignTargeterConfiguration {
public Targeter feignTargeter() {
return new DefaultTargeter();
}
}在HystrixTargeter中,如果没有开启feign.hystrix.enabled配置,那么就进入默认的Feign.Builder.target方法,不过在生产环境中,一般都会开启。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25// HystrixTargeter.java
public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
// 默认情况下是Feign.Builder,所以会进入这个逻辑
if (!(feign instanceof feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder)) {
return feign.target(target);
}
feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder builder = (feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder) feign;
SetterFactory setterFactory = getOptional(factory.getName(), context,
SetterFactory.class);
if (setterFactory != null) {
builder.setterFactory(setterFactory);
}
Class<?> fallback = factory.getFallback();
if (fallback != void.class) {
return targetWithFallback(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallback);
}
Class<?> fallbackFactory = factory.getFallbackFactory();
if (fallbackFactory != void.class) {
return targetWithFallbackFactory(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallbackFactory);
}
return feign.target(target);
}
feign.target(target)方法里,将Feign.Builder中所有的的东西集成在一起,构造一个ReflectiveFeign,调用newInstance方法,传入target生成动态代理
1 | // Feign.java |
调用newInstance方法,传入target,生成ServiceAClient的动态代理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31// ReflectiveFeign.java
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
// 关键代码,接口中的每个方法的名称,对应一个处理这个方法的SynchronousMethodHandler
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
// 接口中的每个方法对应的Method对象,对应一个处理这个方法的SynchronousMethodHandler
// 到时候每一个handler,都会去触发真正的调用
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
// 反射遍历ServiceAClient的方法
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
// 基于工厂创建的InvocationHandler,JDK动态代理的组件, 这里是ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
// 基于JDK的动态代理创建了一个动态代理对象,这个proxy对象,就实现了ServiceAClient接口
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler);
for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}创建完成后,对象被放入Sping容器中,可以被其他类注入使用。
画图总结