聚合
聚合通常在mysql中是group by,例如统计sum等操作,MongoDB也为我们提供了聚合操作,但是实现却不一样。
group()
这次需要的数据会比较多,这次直接用js来准数据。
1
2
3
4
| for(var i = 1; i < 30; ++i ) {
var count = i % 5;
db.mygroup.insert({name: 'name' + i, count : count});
}
|
mongo3.4开始,这个方法已经被官方弃用了,用db.collection.aggregate()替代了,不过这里的例子仍然以db.collection.group()进行讲解。
实例-计数
我们需要按照count字段进行分组然后统计每个分组的数量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| > db.mygroup.group({key: {count:true}, initial: {totalCount:0}, reduce: function(current, aggregator){
... aggregator.totalCount++;
... }});
[
{
"count" : 1,
"totalCount" : 6
},
{
"count" : 2,
"totalCount" : 6
},
{
"count" : 3,
"totalCount" : 6
},
{
"count" : 4,
"totalCount" : 6
},
{
"count" : 0,
"totalCount" : 5
}
]
|
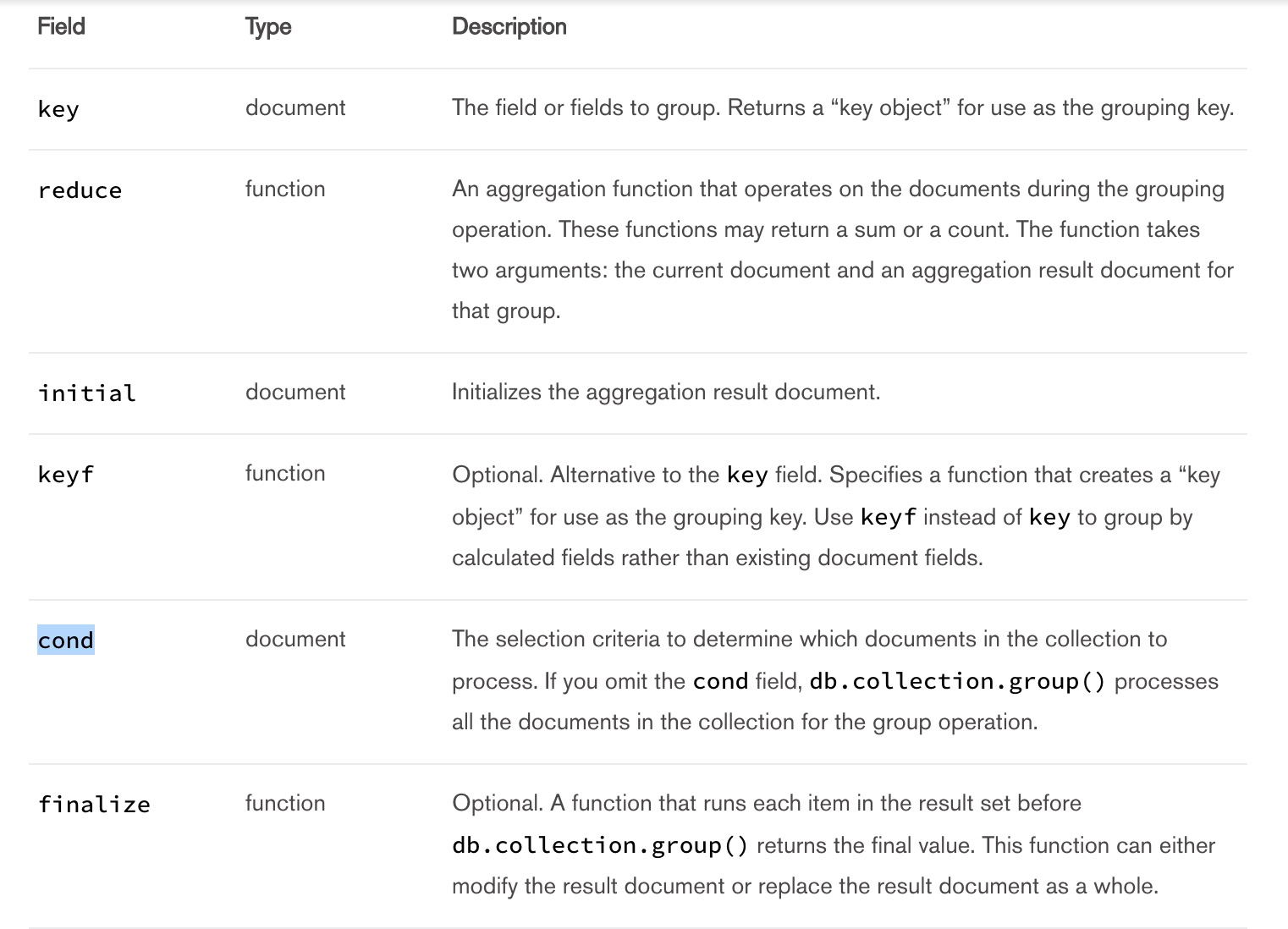
参数解释:
- key: 需要分组的字段
- initial:每一组初始化的值
- reduce:计算
- keyf:二次计算然后产生的key值
- cond:查询条件
- finalize:完成器,在返回之前对结果进行计算
reduce的两个参数,就是分组后对数据的处理,current表示每次循环的当前对象,aggregator则每一组拥有一个共享对象,所以在这个例子里aggregator的totalCount每一组开始循环的时候都是0,最终统计出来每一组的总数。
关于这些的详细介绍,官网文档也给了非常好的介绍:https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/method/db.collection.group/index.html
实例-最大值
重新准备数据:
1
2
3
4
5
| db.mygroup.drop()
for(var i = 1; i < 30; ++i ) {
var count = i % 5;
db.mygroup.insert({name: 'name' + i, age:i, count : count});
}
|
以count作为分组,取出每一组里age最大值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| > db.mygroup.group({key: {count:true}, initial: {maxAge:-1}, reduce: function(current, aggregator){
... if(current.age > aggregator.maxAge) {
... aggregator.maxAge = current.age
... }
... }});
[
{
"count" : 1,
"maxAge" : 26
},
{
"count" : 2,
"maxAge" : 27
},
{
"count" : 3,
"maxAge" : 28
},
{
"count" : 4,
"maxAge" : 29
},
{
"count" : 0,
"maxAge" : 25
}
]
|
实例-找最小值
找出年龄最小值,这里优化一下效率
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| > db.mygroup.group({key: {count:true}, initial: {minAge:0, count:0}, reduce: function(current, aggregator){
... if(aggregator.count == 0) {
... aggregator.minAge = current.age;
... aggregator.count++;
... }else if(current.age < aggregator.minAge) {
... aggregator.minAge = current.age
... aggregator.count++;
... }
... }});
[
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 1
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 2
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 3
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 4
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 5
}
]
|
实例4-平均值
这个例子需要使用finalize完成器来做,先用reduce来完成计数和求和的操作,然后用finalize完成器来求平均值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| > db.mygroup.group({key: {count:true}, initial: {minAge:0, count:0, totalAge:0,totalCount:0}, reduce: function(current, aggregator){
... if(aggregator.count == 0) {
... aggregator.minAge = current.age;
... aggregator.count++
... }else if(current.age < aggregator.minAge) {
... aggregator.minAge = current.age
... aggregator.count++
... }
... aggregator.totalCount++;
... aggregator.totalAge += current.age;
... }, finalize: function(aggregator) {
... aggregator.avgAge = aggregator.totalAge / aggregator.totalCount;
... }});
[
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 1,
"totalAge" : 81,
"totalCount" : 6,
"avgAge" : 13.5
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 2,
"totalAge" : 87,
"totalCount" : 6,
"avgAge" : 14.5
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 3,
"totalAge" : 93,
"totalCount" : 6,
"avgAge" : 15.5
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 4,
"totalAge" : 99,
"totalCount" : 6,
"avgAge" : 16.5
},
{
"count" : 1,
"minAge" : 5,
"totalAge" : 75,
"totalCount" : 5,
"avgAge" : 15
}
]
|
mapReduce
mapReduce主要分为两个阶段,mapReduce在mongodb中可以在分片的环境中运行,而group则不行。
- map阶段
处理数据,例如分组,转换等
- reduce阶段
根据map的输出计算数据,得到想要的结果
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/command/mapReduce/index.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| db.runCommand(
{
mapReduce: <collection>,
map: <function>,
reduce: <function>,
finalize: <function>,
out: <output>,
query: <document>,
sort: <document>,
limit: <number>,
scope: <document>,
jsMode: <boolean>,
verbose: <boolean>,
bypassDocumentValidation: <boolean>,
collation: <document>
}
)
|

For those keys that have multiple values, MongoDB applies the reduce phase, which collects and condenses the aggregated data.
map的结果只有一个值的话,是不会运行reduce的。
实例1-求长度
数据准备:
1
2
3
4
| for(var i = 1; i < 10; ++i ) {
var count = i % 3;
db.student.insert({name: 'name' + i, age:i, count : count});
}
|
现在用MapReduce来统计每一组数据长度。
map必须调用emit函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| > db.getCollection('student').mapReduce(function(){emit(this.count, 1)}, function(key, values){return values.length;}, {out:"length"})
{
"result" : "length",
"timeMillis" : 58,
"counts" : {
"input" : 9,
"emit" : 9,
"reduce" : 3,
"output" : 3
},
"ok" : 1
}
|
注意out指定的是一个collection,MapReduce会把结果生产到当前db的out属性指定的集合里。
1
2
3
4
| > db.length.find();
{ "_id" : 0, "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : 1, "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : 2, "value" : 3 }
|
实例2-求和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| > db.getCollection('student').mapReduce(function(){emit(this.count, this.age)}, function(key, values){var totalAge = 0; for (i = 0; i < values.length; i++){totalAge += values[i]} return totalAge;}, {out:"totalAge"});
{
"result" : "totalAge",
"timeMillis" : 53,
"counts" : {
"input" : 9,
"emit" : 9,
"reduce" : 3,
"output" : 3
},
"ok" : 1
}
> db.totalAge.find();
{ "_id" : 0, "value" : 18 }
{ "_id" : 1, "value" : 12 }
{ "_id" : 2, "value" : 15 }
|
实例3-求最大值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| var maxFun = function(key, values){
var maxAge = 0;
values.forEach(function(current) {
if(current>maxAge){
maxAge = current;
}
});
return maxAge;
};
db.getCollection('student').mapReduce(function(){emit(this.count, this.age)}, maxFun, {out:"maxAge"});
> db.getCollection('maxAge').find({})
{ "_id" : 0, "value" : 9 }
{ "_id" : 1, "value" : 7 }
{ "_id" : 2, "value" : 8 }
>
|
实例4-求平均数
求平均数也很简单,就是把和除以长度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| > var avgFun = function(key, values){var totalAge = 0; for (i = 0; i < values.length; i++){totalAge += values[i]} return totalAge / values.length;};
> db.getCollection('student').mapReduce(function(){emit(this.count, this.age)}, avgFun, {out:"avgAge"});
> db.avgAge.find();
{ "_id" : 0, "value" : 6 }
{ "_id" : 1, "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : 2, "value" : 5 }
|
实例5-标签统计
数据准备:
1
2
3
4
5
| db.getCollection('article').insert({name:"article1", tags:['java','python','mongodb','ruby']});
db.getCollection('article').insert({name:"article2", tags:['perl','scala','mongodb','ruby']});
db.getCollection('article').insert({name:"article3", tags:['perl','kotlin','mongodb','ruby']});
db.getCollection('article').insert({name:"article4", tags:['perl','kotlin','mongodb','groovy']});
db.getCollection('article').insert({name:"article5", tags:['perl','kotlin','redis','groovy']});
|
每个文章都有标签,现在要统计每一个标签出现的次数。
有思路吗?这个用mongodb来做实在是太方便了,如果是传统的sql,可能还要好好想想,我们在map的时候,就用每一个tag分组,得到我们要的数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| db.article.mapReduce(function(){
this.tags.forEach(function(currrnt){
emit(currrnt, 1)
});
}, function(key, values){
return values.length;
}, {out:"aa"});
> db.aa.find();
{ "_id" : "groovy", "value" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "java", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "perl", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "python", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "redis", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "ruby", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "scala", "value" : 1 }
|
finalize使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| db.article.mapReduce(function(){
this.tags.forEach(function(currrnt){
emit(currrnt, 1)
});
}, function(key, values){
return values.length;
}, {out:"aa"});
> db.getCollection('aa').find({})
{ "_id" : "groovy", "value" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "java", "value" : { "count" : 1 } }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "perl", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "python", "value" : { "count" : 1 } }
{ "_id" : "redis", "value" : { "count" : 1 } }
{ "_id" : "ruby", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "scala", "value" : { "count" : 1 } }
|
为什么会出现这样的结果?有的是对象,有的是值,之前说过,如果map产出的values的结果只有一个,是不会执行reduce阶段的,这里可以用finalize来保证结果的统一。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| db.article.mapReduce(function(){
this.tags.forEach(function(currrnt){
emit(currrnt, {count:1})
});
}, function(key, values){
return values.length;
}, {out:"aa",finalize: function(key,reduced){
if(reduced.count) {
return reduced.count;
}
return reduced;
}});
> db.getCollection('aa').find({})
{ "_id" : "groovy", "value" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "java", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "perl", "value" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "python", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "redis", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "ruby", "value" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "scala", "value" : 1 }
|
进阶,mapReduce过滤
现在我们只统计发布了java标签的数据,可以用query参数来过滤,也可以用map阶段来用代码过滤。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| db.article.mapReduce(function(){
var flag = false;
for(i in this.tags){
if(this.tags[i] == 'java') {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
this.tags.forEach(function(tag){
emit(tag, {count:1});
});
}
}, function(key, values){
return values.length;
}, {out:"aa",finalize: function(key,reduced){
if(reduced.count) {
return reduced.count;
}
return reduced;
}});
> db.getCollection('aa').find({})
{ "_id" : "java", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "python", "value" : 1 }
|
聚合框架(aggregation framework)
聚合框架是mongo聚合操作的第三种方式,它与group()解决的问题是的一样的,group()和MapReduce都是需要写函数的,所以mongodb提供了聚合框架,简化聚合操作。
注意:只有MapReduce和聚合框架能分片的环境下使用。
聚合框架是不能自定义函数的,它帮我们实现了一些函数。
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/core/aggregation-pipeline/index.html

聚合框架为我们提供了很多操作,aggregate参数是一个pipeline,每一个按操作按顺序执行。
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/operator/aggregation/
常用的几个操作:
实例1-长度
数据准备:
1
2
3
4
5
| db.commodity.insert({category:1, price:200, name: 'name1'});
db.commodity.insert({category:1, price:300, name: 'name2'});
db.commodity.insert({category:2, price:100, name: 'name3'});
db.commodity.insert({category:2, price:500, name: 'name4'});
db.commodity.insert({category:3, price:200, name: 'name5'});
|
按照category分组并统计每一组的长度
1
2
3
4
| > db.commodity.aggregate({$group: {_id:'$category', totalCount: {$sum:1}}});
{ "_id" : 3, "totalCount" : 1 }
{ "_id" : 2, "totalCount" : 2 }
{ "_id" : 1, "totalCount" : 2 }
|
实例2-求和
1
2
3
4
| > db.commodity.aggregate({$group: {_id:'$category', totalCount: {$sum:1}, totalPrice: {$sum: '$price'}}});
{ "_id" : 3, "totalCount" : 1, "totalPrice" : 200 }
{ "_id" : 2, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 600 }
{ "_id" : 1, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 500 }
|
在没有指定排序规则的时候,aggregate是不保证排序的,需要用$sort指定排序。
1
2
3
4
| > db.commodity.aggregate({$group: {_id:'$category', totalCount: {$sum:1}, totalPrice: {$sum: '$price'}}}, {$sort: {'totalPrice':-1}});
{ "_id" : 2, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 600 }
{ "_id" : 1, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 500 }
{ "_id" : 3, "totalCount" : 1, "totalPrice" : 200 }
|
实例3-求平均值
1
2
3
4
| > db.commodity.aggregate({$group: {_id:'$category', totalCount: {$sum:1}, totalPrice: {$sum: '$price'}, avgPrice: {$avg:'$price'}}}, {$sort: {'totalPrice':-1}});
{ "_id" : 2, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 600, "avgPrice" : 300 }
{ "_id" : 1, "totalCount" : 2, "totalPrice" : 500, "avgPrice" : 250 }
{ "_id" : 3, "totalCount" : 1, "totalPrice" : 200, "avgPrice" : 200 }
|
实例4-标签统计
之前在演示MapReduce的时候,用MapReduce对article的tags统计tag出现的次数,这里用聚合框架来达到同样的效果,当然想到的就是之前介绍到的$unwind操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| > db.article.aggregate({$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}});
{ "_id" : "redis", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "groovy", "total" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "scala", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "perl", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "python", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "java", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "ruby", "total" : 3 }
|
实例5-标签过滤
找出打了java标签的文章并进行统计
1
2
3
4
5
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$in:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}});
{ "_id" : "ruby", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "python", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "java", "total" : 1 }
|
实例6-各种操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$nin:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}}, {$sort:{'total':-1}});
{ "_id" : "perl", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "groovy", "total" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "ruby", "total" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "redis", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "scala", "total" : 1 }
|
取前三:
1
2
3
4
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$nin:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}}, {$sort:{'total':-1}}, {$limit:3});
{ "_id" : "perl", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "total" : 3 }
|
取第二到到第四:
1
2
3
4
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$nin:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}}, {$sort:{'total':-1}},{$skip:1} ,{$limit:3});
{ "_id" : "mongodb", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "kotlin", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "groovy", "total" : 2 }
|
只显示total:
1
2
3
4
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$nin:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}}, {$sort:{'total':-1}},{$skip:1} ,{$limit:3}, {$project:{_id:0}});
{ "total" : 3 }
{ "total" : 3 }
{ "total" : 2 }
|
把total加100
1
2
3
4
| > db.article.aggregate({$match:{'tags' : {$nin:['java']}}}, {$unwind: '$tags'}, {$group: {_id:'$tags', total:{$sum: 1}}}, {$sort:{'total':-1}},{$skip:1} ,{$limit:3}, {$project:{_id:0,hello:{$add:['$total',100]}}});
{ "hello" : 103 }
{ "hello" : 103 }
{ "hello" : 102 }
|
